
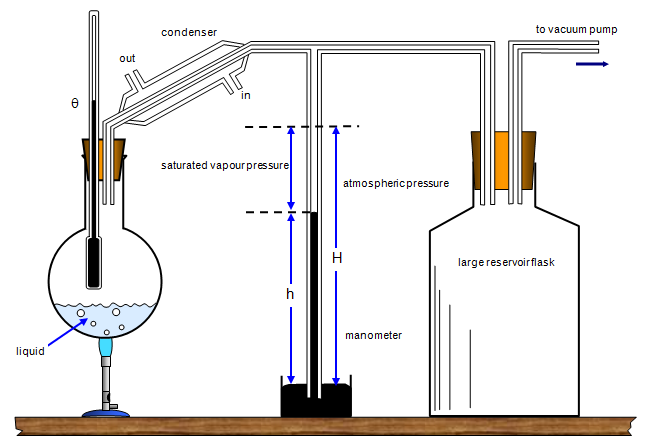
The liquid in the flask
is heated until it boils and the pressure (h) within the apparatus measured with a manometer.
Saturated pressure = H - h
The large flask is included in the apparatus to
minimise the effects of rapid changes of pressure during the experiment. The source of heat
is then removed and the flask allowed to cool slowly. Boiling can be achieved at any
temperature by reducing the pressure within the apparatus using the vacuum pump.
The water can be made to boil at 30 oC with a simple tap-mounted
pump, the s.v.p. of water being about 3 cm of mercury at this temperature.