The Law of conservation of momentum
The law of conservation of
momentum states that :-
Momentum is conserved in ALL collisions or explosion in an isolated system where no external forces act. In other words the momentum before the collision or explosion is the same as that after it even if the kinetic energy is not conserved.
Collisions
Elastic and inelastic collisions
In a collision the kinetic energy is sometimes the same before the collision
as it is afterwards - such a collision is called an elastic collision. Perfectly elastic collisions are
rare - usually some of the kinetic energy is converted to sound or heat. Even a trampolinist
colliding with a trampoline bed loses energy as the bed stretches and heats up. A perfectly
inelastic collision is one where all the kinetic energy is converted into other forms - a piece of
soft putty falling onto the floor is an almost perfectly inelastic collision, the kinetic energy of the
moving putty is converted into heat and a little sound as the putty is deformed on impact. Most real
collisions are usually somewhere between the two extremes.
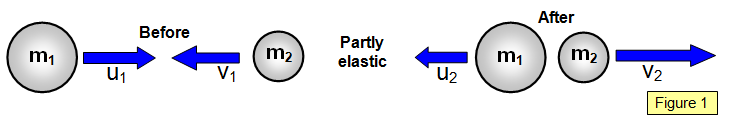
In all collisions the law of
conservation of momentum applies. If a mass m1 moving at a velocity u1 collides
with a mass m2 moving at a velocity u2 such that after the collision m1
moves at v1 and m2 moves at v2 then:-
momentum before collision = momentum after collision
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
The law of conservation of momentum applies whether
the collisions are elastic or not. (See Figure 1)
The special case of two equal masses making a
completely elastic collision is shown in Figure 2.
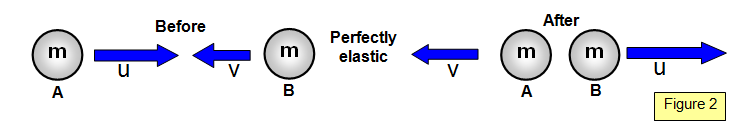
Notice that the velocities of the two bodies A and B are
swapped over.
Inelastic collisions
As we have said in an inelastic collision
some, or all, the kinetic energy of the colliding bodies is lost - this may be converted into heat or
used to deform the bodies. Imagine two balls colliding head on, sticking together and then moving
off after the collision (See Figure 3).

The total momentum before collision must be equal to
the total momentum after collision and if we know the masses and velocities of the colliding
objects before collision we can use this principle to find out how fast they are moving - and in
which direction - after the collision.
Example problem
If a mass of 3.5 kg is moving left to right at 5 ms-1 collides with a mass of 4.0 kg moving right to left at 3.0 ms-1 and they stick together find the final velocity of the combined masses.
Momentum before impact = 3.5x5.0 + [-4.0x3.0] = 5.5 Ns but this must equal the momentum after the collision i.e. total mass x final velocity.
Notice that one of the velocities is negative showing that the ball was moving right to left.
Mass afterwards = 7.5 kg
Therefore velocity afterwards = 5.5/7.5 = 0.73 ms-1 this is positive showing that after collision the combined two balls move from left to right.
The amount of kinetic energy lost in a collision
depends on the nature of both objects involved in the collision. For example a different amount of
energy will be converted into heat and sound if putty is dropped onto putty than if putty is dropped
onto steel. The energy conversions will also be different for steel on steel, velcro on velcro
etc.
Remember that velocity and momentum are vector
quantities and must be treated as such in all collision
problems.
Example problems
1. A rifle of mass 3 kg fires a bullet of mass 50 gm (0.05 kg) at 100 ms-1.
(a) Calculate the recoil velocity of the rifle
(b) explain why it is better to hold the rifle into your shoulder when firing it.
(a) recoil velocity (V) = -vm/M = 100x0.05/3 = 1.67 ms-1
(b) if the rifle is in contact with your shoulder when it is fired the mass that recoils is the mass of the rifle plus your mass. If your mass is 50 kg then:
Recoil velocity = - 0.05x100/53 = 0.09 ms-1 much less then before!
2. A bullet of mass 0.05 kg moving at 100 ms-1 strikes a block of wood and is embedded in it to a depth of 5 cm. If the wood has a mass of 2.5 kg calculate:-
(a) the velocity of the block and bullet after the collision
(b) the mean retarding force of the bullet
(a) Using: velocity (V) = vm/M = 100x0.05/2.5 = 2 ms-1
(b) Using: - Kinetic energy lost = Retarding force (F) x distance
Therefore 250 -10.2 = 239.8 = Fx0.05
Retarding force = 4796 N
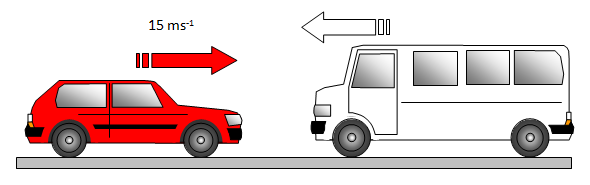
3. A car of mass 1000 kg travelling from west to east along a road at 15 ms-1 collides with a van of mass 3000 kg travelling in the opposite direction. If they both come to rest after the collision what was the initial velocity of the van?
Momentum after the collision = 0 so momentum before collision must also equal 0. Therefore :
Momentum before collision = momentum of car + momentum of van = 1000x15 + 3000v where v is the velocity of the van.
This gives 1000x15 + 3000v = 0 and so v = - 1000x15/3000 = -5 ms-1
the negative sign meaning that it was travelling in the opposite direction i.e. east to west.
A VERSION IN WORD IS AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS USB