
Three characteristics are usually
measured and these are shown in Figure 2:
(a) the variation of base current
(IB) with base- emitter voltage (VBE),
(b) the variation of collector
current (IC) with base current, and
(c) the variation of collector current
with collector- emitter voltage (VCE).
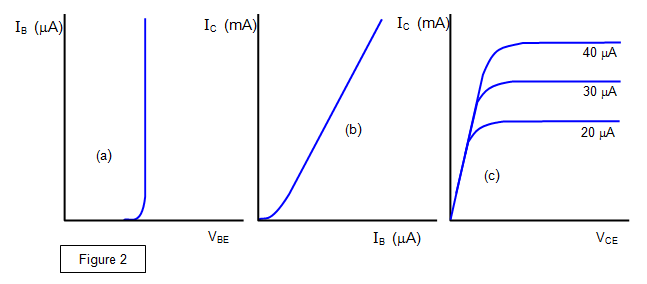
Figure 2(a) shows the 'switching on' of
the transistor. There is no significant base current until the base-emitter voltage reaches
about 0.6 V.
Figure 2(b) shows how the collector current varies when there is a change
in the base current. You can see that a change in base current (ΔIB) of a few microamps will produce a collector
current change (ΔIC) of a few miiliamps. This
shows the amplifying action of the transistor and also that this amplification is current-
controlled rather than voltage-controlled. The ratio of the change in collector current to the
change in base current is called the current gain of the transistor, and is written as
hFE.
This usually has a value of between 100 and 200 for an npn silicon
transistor.
Figure 2(c) shows the variation of collector current with collector-emitter
voltage. There are several curves, each representing a different base current.