
In the thermionic diode a beam of electrons
moves a cross the tube and hits the positive anode. If a hole is made in the anode
the electrons will go through it and a stream of electrons will emerge on the other side. This
device is called an electron gun.
The anode is made cylindrical as shown in
the diagram. A high voltage, often as high as 3000 V, is connected between the cathode and
the anode and this accelerates the electrons to a high speed – around 30 000 000 m/s or
about 1/10 of the speed of light!
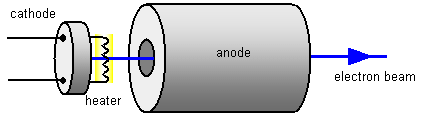
The
beam of electrons is called a cathode ray because it starts from the
cathode.
1. Cathode rays are beams of fast moving electrons
2. Increasing the
heater voltage heats the cathode more and so it gives out more electrons. This makes the
beam stronger (brighter)
3. Increasing the anode voltage makes the electrons move
faster by giving them more energy
4. Cathode rays do not pass through glass or
metal
5. Cathode rays travel in straight lines in a vacuum
6. Cathode rays travel in
circles in magnetic fields
7. Cathode rays travel in parabolas in electric fields
8.
The range of cathode rays in gases increases as the energy of the
electrons increases.