
The simplest form of graph that describes the way
an object is moving is a distance-time graph. The distance that and object has moved is
plotted on the Y-axis and the time is plotted on the X-axis.
The graphs below show
you how the distance changes with time for a number of different
examples.
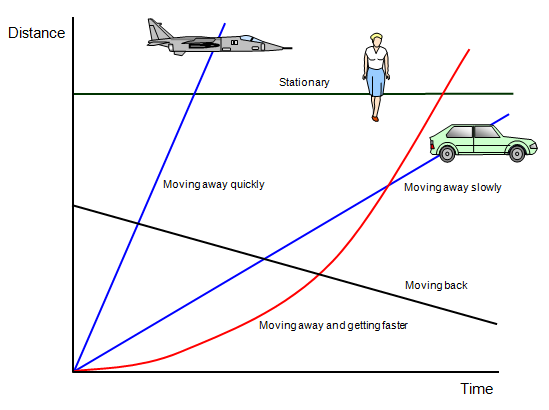
Imagine that the
distance axis shows how far an object is away from you.
The horizontal straight line
shows something that stays at the same distance from you all the time – the object is
stationary.
Straight lines slanting upwards show objects moving away from you at a
steady speed while straight lines slanting downwards show objects moving towards you at a
steady speed. The steeper the line the faster the object is moving.
A curved line
shows an object whose speed is changing as time goes by.
We can use these
graphs to work out the speed of an object.
This is easy to do for a straight-line graph but for the curved line the speed is constantly changing and so we must measure the change in speed over a small time interval to get an accurate answer.