
You probably know that when you use a simple
pump to pump up a bicycle tyre the pump gets hot. This is because when a gas gets
compressed its temperature rises; the reverse of this also happens when a gas is expanded,
its temperature falls. The gas molecules gain energy from, or lose energy to, the moving
walls of their container.
These effects can be noticed in the refrigerator, in weather and
in the cloud chamber used in nuclear physics.
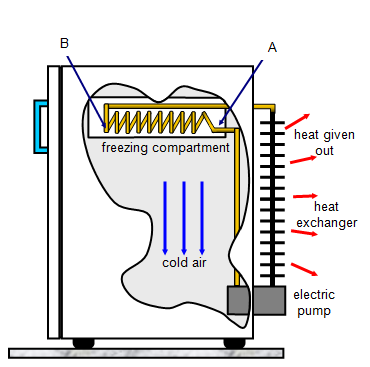
In a refrigerator, heat is removed from the
surroundings at one point, the freezing compartment, and given out to the surroundings at
another, the heat exchanger. A volatile liquid called freon evaporates through a small hole
(A) into the coils (B) because of the low pressure in B. As it does so it cools down taking
latent heat from its surroundings and so the freezing compartment gets colder. The pump
then forces this cold vapour into the heat exchanger coils where it is compressed and
liquifies giving out latent heat to the surroundings. The whole cycle is then repeated. The
heat exchanger coils get quite hot and for this reason 'fridges and freezers should not be
placed with their heat exchangers close to a wall otherwise they may overheat.
Notice that the freezing compartment is at the top of the fridge, the cold air
produced there will sink to the bottom keeping the whole fridge cold.
Freon is a
name for a collection of different gases that are suitable for refrigerators. These gases used
contain harmful CFCs but these have now been banned and replaced with a safer
alternative.
A given volume of air at a certain temperature can only hold a certain amount of water vapour. In Figure 2(a) there is an unlimited volume of air above the open beaker and so water is lost by evaporation. In (b) there is a limited volume of air above the water in the enclosed space and so after a while the water vapour creates a pressure that prevents any further net evaporation.
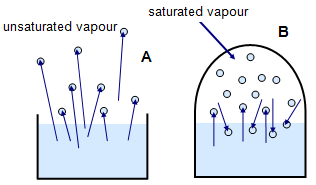
The water vapour at A
is called an UNSATURATED VAPOUR and that at B a SATURATED
VAPOUR. The hotter the air the more water vapour it can hold. The pressure of the
saturated vapour will be greater at higher temperatures.
The amount of
water vapour in the air is called the HUMIDITY. If the humidity is high there is a lot of water
vapour in the air and so further evaporation is difficult. This is why it is difficult to lose water
vapour by sweating when the humidity is high. If a saturated vapour is cooled then some of
the liquid will condense - a good example of this is in the way clouds form.
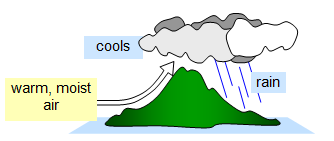
As warm, moist air rises it cools, is unable to hold
so much water and so the water condenses as millions of minute droplets - clouds. As more
condenses the cloud cannot support itself and so the water falls to the ground as
rain.
This lovely toy also works because of evaporation - this time the evaporation of ether. Ether evaporates from the body of the bird pushing liquid ether into the head making it top heavy and so the bird tilts forwards. The head is kept cool by water and so the liquid does not evaporate but runs back into the body and so the whole process starts all over again. Using meths in the glass will make the bird bob up and down quicker because the meths evaporates more rapidly.