
In 1932 Carl Anderson discovered the positron. The positron is a particle of antimatter and it was the first known particle of antimatter to be found.
A positron has the same mass as an electron but a positive charge.
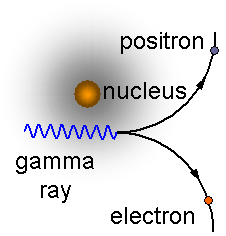
A high-energy gamma ray passing close to a nucleus can turn into to particles - an electron (matter) and a positron (antiimatter).
When a particle (say a proton) meets its antiparticle (an antiproton) they destroy each other producing a flash of energy - usually gamma rays.
Electron-positron annihilations have been observed in the laboratory.