Velocity-time graphs
A useful form of graph that describes the way an
object is moving is a velocity-time graph. The velocity of the object at any moment is plotted
on the Y-axis and the time is plotted on the X-axis.
The graphs below show you how
the velocity changes with time for a number of different
examples.
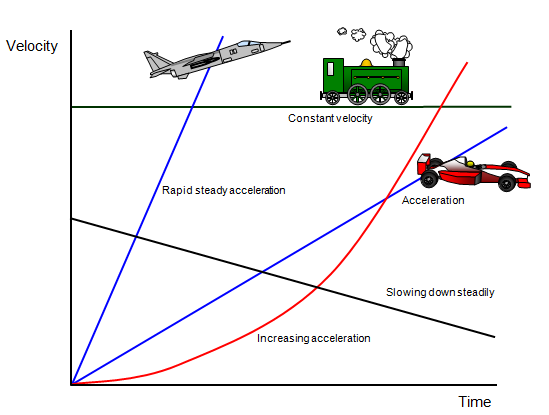
The horizontal
straight line shows something that is moving with a constant velocity.
Straight lines
slanting upwards show objects whose velocity is increasing at a steady rate – they have
constant positive acceleration. Straight lines slanting downwards show objects whose
velocity is decreasing at a steady rate – they have a constant negative acceleration
(retardation). The steeper the line the greater the acceleration or retardation.
A
curved line shows an object whose acceleration is changing as time goes by.
We
can use these graphs to work out the acceleration of an object.
Acceleration = change in velocity/time
and so the gradient of the line (change in velocity/time) gives us the acceleration
This is easy to do for a straight-line graph but for
the curved line the acceleration is constantly changing and so we must measure the change
in velocity over a small time interval to get an accurate answer.