
If an object is in a position where it could do work if released then it has POTENTIAL ENERGY (sometimes written as p.e).
The energy associated with the position of a body of mass m in a gravitational field is the gravitational potential energy of the body compared with some reference point where h = 0, usually the surface of the Earth.
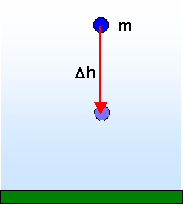
The energy is converted to other forms when the gravitational potential energy changes due to a movement within the field. If the distance moved parallel to the gravitational field is Dh then the change in potential energy is:
It is important to realise that Dh is measured parallel to the field. Any other direction of movement will cause a smaller change in the gravitational potential energy and a body that moves at right angles to the field will have no change at all in their gravitational potential energy.
This means that it does not matter which route the object takes when moving from one point in the field to another.