
When a wire carrying a current is placed in a magnetic field the wire experiences a force due to the interaction between the field and the moving charges in the wire.

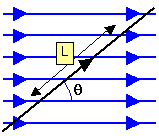
The force F on the wire can be shown to be proportional to
(a) the current on the wire I,
(b) the length of the conductor in the field L,
(c) the sine of the angle that the conductor makes with the field q, and
(d) the strength of the field - this is measured by a quantity known as the magnetic flux density B of the field, measured in Tesla