Rectification
For heating and lighting a.c. is just as good as d.c. but for some
uses d.c. is needed.
Televisions, radios, battery chargers and electroplating apparatus
need d.c. It is therefore useful to be able to convert a.c. into d.c. This can be done with a
DIODE and the process is called RECTIFICATION.
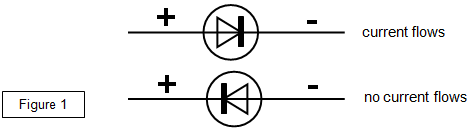
A diode is a device that allows electricity to flow through it in one direction only
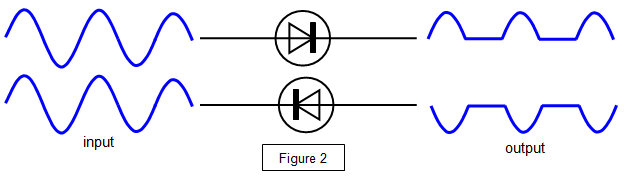
So if a.c. is applied to the diode only half of it gets
through.
You can see how the positive or the negative part of the a.c. cycle can be
allowed through simply by turning the diode round.
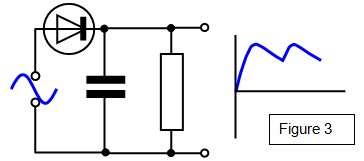
This type of output is known as
HALF
WAVE RECTIFICATION. Although the current is not steady it now only flows in one
direction.
If a capacitor is added to the circuit as shown then the output voltage is
smoothed.
In half wave
rectification only half the a.c. cycle is used, the other half being blocked by the diode.
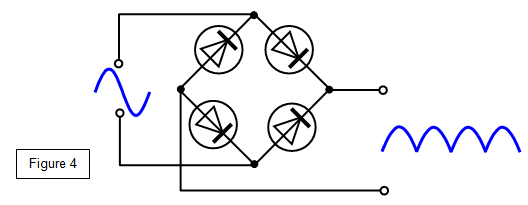
By using the circuit below, both half cycles are used.
This type of
output is known as
FULL WAVE RECTIFICATION and the device producing it is
called a bridge rectifier (Figure 5).
A VERSION IN WORD IS AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS USB